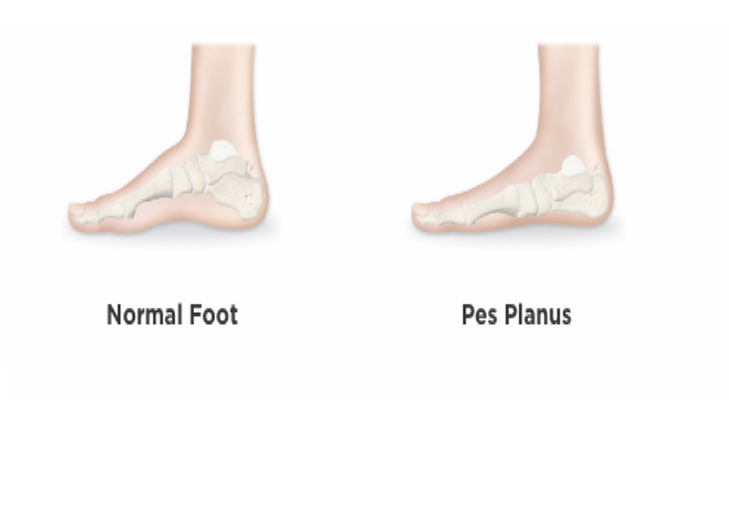
Pes Panus deformity is more commonly known as flatfoot. Both children and adults may be flat-footed, and it’s estimated that the prevalence of Pes Planus in the general population is about 20-30%.
What causes Pes Planus?
The foot must act as a reliable landing point when putting the foot down, usually heel first, and as a rigid taking off point when walking or running. In pathological flatfoot, the arch of one foot or both feet have either not developed normally, or an injury or condition has produced it, such as rheumatoid arthritis, stroke or diabetes. It may develop as a result of degenerative changes in joints and/or ligaments; this will tend to be in older patients and people who are very heavy. It may also occur as a result of trauma to the bones and/or ligaments. An increasingly common cause seems to be neuropathic problems secondary to diabetes, as an early manifestation of Charcot foot.
Pes Planus symptoms
The arch of the foot is lowered or flattened out, depending on the severity. Slightly lowered arches are usually symptom free. Issues such as discomfort and chronic pain can arise if there is a minor injury, sudden weight gain, poorly-fitted footwear, and excessive standing, walking, jumping or running.
Pes Planus diagnosis
Pes Planus diagnosis is usually by clinical examination. In young people, the flat foot that is apparent when standing disappears when they stand on tip toe, and the normal arch appears. This is flexible Pes Planus, is usually symptomless and requires no treatment. X-rays may be helpful when there is a history of injury but may not be necessary.
Pes Planus treatment
Management in less severe cases of Pes Planus generally consists of wearing spacious, comfortable footwear with good arch support, possibly supplemented by padding or orthotics in order to balance and cushion the foot. The object of Pes Planus treatment is to restore anatomy and function as much as possible. Orthopedic surgery, sometimes with osteotomy, may be necessary. Bone grafting to replace lost bone may be also necessary. After surgery, your child may need to wear orthotics. Since each case is different and there are many types of treatments, discuss the best treatment for your child with your doctor and orthopedic surgeon.
Pes Planus deformity complications
If not treated, some cases of Pes Planus can result in severe deformity and early onset of arthritis of the foot and ankle. This may cause severe pain and significantly reduce the ability to walk, even when wearing orthotics.
 Share on facebook
Share on facebook
 Share on twitter
Share on twitter
 Share on linkedin
Share on linkedin
 Share on email
Share on email